Humanity could soon live inside asteroids, bizarre new study suggests
The past two years were all about billionaires in the sky. Be it tone-deaf Jeff Bezos’ historical—and hysterical—space flight, Sir Richard Branson’s sibling rivalry-fuelled orbital debut, or Elon Musk’s first-ever all-civilian crew, the possibilities of space colonisation seemed so close yet so far.
Heck, late 2021 also saw Japanese business magnate Yusaku Maezawa handing out cash from the cosmos and even hosting a “match-making event” just so that he could find a female “life partner” to accompany him to the moon. Oh, to be a single billionaire in space.
Then came the so-called “New Space” movement, where aerospace companies increasingly aimed to develop low-cost access to the interstellar for everyone on Earth. But ultimately, humanity’s quest to become a multi-planetary species requires the establishment of viable habitats. Although the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has already gotten a head start with its research into 3D-printed bases on the moon and Mars, the concept of space cities continues to exist solely in science fiction today.
However, new research by scientists at the University of Rochester, New York, suggests that our future may just lie in… asteroids. Yes, the same chunks of space rocks that allegedly wiped out dinosaurs and now keep buzzing past Earth almost every other day.
O’Neill cylinder and spinning space settlements
In their “wildly theoretical” study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, the team of researchers outlined a plan for hollowing out asteroids and turning them into spinning space cities with artificial gravity.
The concept essentially builds on an idea called the ‘O’Neill cylinder’. In 1972, NASA reportedly commissioned physicist Gerard O’Neill to design a space habitat that could feasibly allow humans to settle in space. The expert and his colleagues then sketched plans for a rotating space colony that consisted of two cylinders rotating in opposite directions—with a rod connecting at each end.
The cylinders would rotate fast enough to provide artificial gravity on their inner surface but slow enough so that people living in them would not experience motion sickness.

You would have seen O’Neill cylinder-like habitats featured in movies like Star Trek and Interstellar. Both Bezos and Musk have also referenced the spinning space metropolises in their visions for future space habitats. “Our paper lives on the edge of science and science fiction,” said co-author author Adam Frank in a statement. “We’re taking a science fiction idea that has been very popular recently—in TV shows like Amazon’s The Expanse—and offering a new path for using an asteroid to build a city in space.”
Although the O’Neill cylinder is a fascinating idea, transporting necessary building materials to space in a cost-effective manner would be difficult. This is where asteroids make their debut. “All those flying mountains whirling around the sun might provide a faster, cheaper, and more effective path to space cities,” Frank said. “Based on our calculations, a 300-metre-diameter asteroid just a few football fields across could be expanded into a cylindrical space habitat with about 22 square miles of living area—roughly the size of Manhattan.”
Rubble piles and the list of pros and cons
As of today, scientists estimate that there are about 1,000 asteroids in our solar system alone. Besides their abundance, the space rocks also sport a layer that acts as a natural shield against deadly cosmic radiation from the sun—in turn, making them ideal for human habitation.
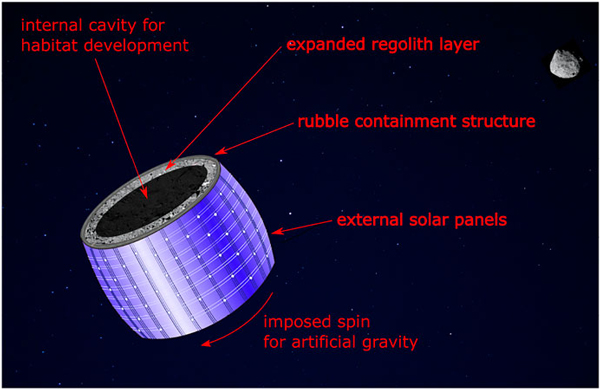
At the same time, however, one major con of asteroids is that they’re not strong enough to handle even one-third of Earth’s gravity from spinning. “Once an asteroid is set into rotation, it would merely fracture and break,” the University of Rochester noted in its aforementioned statement. “Moreover, most asteroids are not even solid rock but ‘rubble piles’—clusters of loose boulders, stones, and sand held together by the weak mutual gravity of space. If the researchers wanted to make space habitats out of these asteroids, they’d have to figure out how to work with rubble piles.”
Their solution? Covering the chosen asteroid in a flexible mesh bag. Made of ultralight and high-strength carbon nanofibers, the bag would envelope and support the entire mass of the asteroid’s rubble and the habitat within, while also supporting its own weight as it spins. The nanofibers would also be covered with solar panels that will help power the entire space city.
What’s more is that, as a colonised asteroid, the city could further aid interplanetary transport. ‘Revolutionary’ doesn’t begin to describe the innovation in question.
“The idea of asteroid cities might seem too distant until you realise that in 1900 no one had ever flown in an aeroplane, yet right this minute thousands of people are sitting comfortably in chairs as they hurdle at hundreds of miles an hour, miles above the ground,” Frank concluded. “Space cities might seem like a fantasy now, but history shows that a century or so of technological progress can make impossible things possible.”





