New project creates digital clones of human brains to help treat neurological disorders
In 2010, NASA researcher John Vickers introduced the world to the concept of ‘digital twins’—the virtual representation of a physical object or process. With an industry estimated to hit $50 billion by 2026, the concept has now bled into manufacturing and aerospace. In fact, there are even digital doppelgängers of cities, ports and power stations aimed to optimise operations in ways which we could previously only imagine.
Then, in 2016, William Ruh—the ex-CEO of GE Digital (a subsidiary of the American corporation General Electric)—predicted the application of the concept in biology, stating that “we will have a digital twin at birth, and it will take data off of the sensors everybody is running, and that digital twin will predict things for us about disease and cancer and other things.” Simply put, virtual clones of our body could inform us about the development of diseases and suggest tailored medications for the same. The concept also harbours the potential of trialing several treatments on the clone without testing them on the physical body, thereby eliminating the entire risk that comes along with the process.
As of late, research programmes like ECHOES (Enhancing Cardiac care tHrOugh Extensive Sensing) have been in the pursuit of building digital counterparts of human hearts. A recent investigation by WIRED additionally noted how Siemens Healthineers, a medical device company based in Germany, and French software corporation Dassault Systèmes are also part of the same race.
While the latter has teamed up with the US Food and Drug Administration to approve what it terms “The Living Heart,” Austrian company GOLEM is currently creating virtual twins of vulnerable people who live alone. “The idea is that the digital twin continuously monitors their health, alerting caregivers if they fall ill and need help,” WIRED explained.
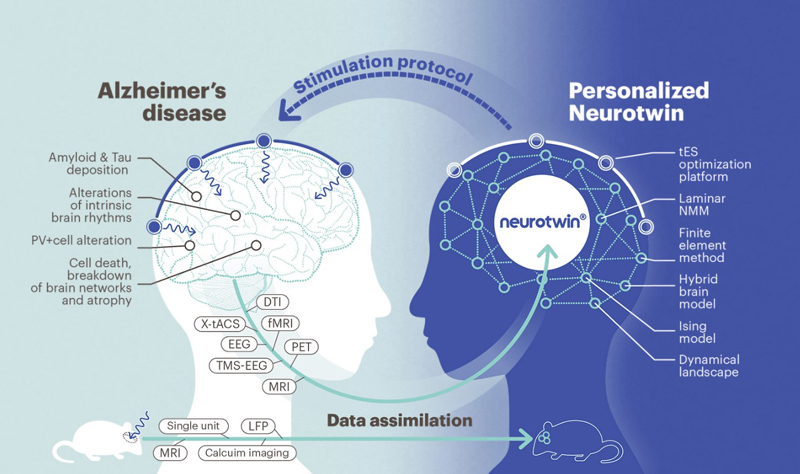
More recently, digital twins have been the focus of a European Union-funded project that seeks to clone a patient’s entire brain. Dubbed Neurotwin, the research project aims to create virtual models that can be used to predict the effects of stimulation for the treatment of neurological disorders—including epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. When it comes to epilepsy, non-invasive stimulations (where electrical currents are painlessly delivered to the brain) have proven effective in tackling seizures. Given how drugs don’t help a third of epilepsy patients, the technology is coveted yet needs refinement. This is where virtual clones come in.
“The digital avatar is essentially a mathematical model running on a computer,” Giulio Ruffini, coordinator of the Neurotwin project, told WIRED. Including a network of embedded “neural mass models,” the technology hopes to create a map of the neural connections in the brain—a concept termed as the ‘connectome’. “In the case of epilepsy, some areas of the connectome could become overexcited,” the outlet mentioned. “In the case of, say, stroke, the connectome might be altered.” Once the digital clone has been created by the team, with about half an hour-worth of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data and ten minutes of electroencephalography (EEG) readings to capture electrical activities and realistically simulate the brain’s main tissues (including the scalp, skull, cerebrospinal fluid, and grey and white matter), it can then be used to optimise stimulation of the real patient’s brain.
According to Ruffini, this is possible “because we can run endless simulations on the computer until we find what we need. It is, in this sense, like a weather forecasting computational model.”
“For example, to improve treatment for an epilepsy patient, the person would wear a headcap every day for 20 minutes as it delivers transcranial electrical stimulations to their brain,” WIRED added. Using the digital twin, on the other hand, Ruffini and his team could optimise the position of stimulating electrodes, along with the level of current applied.
With digital twins of biological organs gaining traction, the technology opens up a conversation about ethics in the upcoming field. For starters, who should own one’s digital clone? The patient in question or the company building it? What will happen to it after the patient dies? And if the patient is predicted to have a stroke in two weeks, shouldn’t they have the right to know or refrain from knowing the same?
As per Matthias Braun, an ethicist at the University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, “In order to not be an infringement on autonomy or privacy, it is important that this specific person has control of the use [of their digital twin].” Not having these rights would result in what the expert calls “digital slavery.”
Nevertheless, Braun believes digital clones offer exciting and revolutionary pathways to develop new treatments. As of today, Neurotwin is planning to kick off clinical trials in 2023 and create virtual clones of around 60 Alzheimer’s patients—who will receive a stimulation treatment that has been optimised specifically for their brain. The second phase of the trials has similar objectives, but for patients with treatment-resistant focal epilepsy.
“Both are proof-of-concept trials to determine whether the approach works and can improve treatment outcomes for these patients,” WIRED concluded. If successful, Ruffini and his team hope to apply the technology to study other aspects of the brain, like those involved in multiple sclerosis, stroke rehabilitation, depression and the effects of psychedelics.